Inflationary Gap
 When aggregate demand is more than
aggregate supply at full level of employment, it is called excess demand and
the gap or excess is called inflationary gap. In an economy, when the actual
gross domestic product exceeds the anticipated gross domestic product at full
employment, it leads to inflationary gap. An important point here is that economy
should be at full employment. This denotes optimum utilisation of resources. For example, demand for grains is 1000 kilograms and
supply is 700 kilograms at full level of employment, the excess of 300 kilograms will be
inflationary gap.
When aggregate demand is more than
aggregate supply at full level of employment, it is called excess demand and
the gap or excess is called inflationary gap. In an economy, when the actual
gross domestic product exceeds the anticipated gross domestic product at full
employment, it leads to inflationary gap. An important point here is that economy
should be at full employment. This denotes optimum utilisation of resources. For example, demand for grains is 1000 kilograms and
supply is 700 kilograms at full level of employment, the excess of 300 kilograms will be
inflationary gap.Deflationary Gap
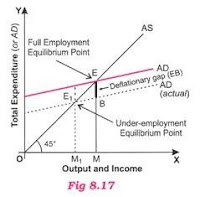 In simple terms, it is the excess of
aggregate supply over aggregate demand at full level of employment. It is the
amount of deficiency of aggregate demand to supply. Deflationary gaps lead to
increasing unemployment, low economic growth rate and fall in price levels. It
is also known as the negative output gap. The gap denotes the amount by which
aggregate demand must increase to increase the level of equilibrium at full
level of employment.
In simple terms, it is the excess of
aggregate supply over aggregate demand at full level of employment. It is the
amount of deficiency of aggregate demand to supply. Deflationary gaps lead to
increasing unemployment, low economic growth rate and fall in price levels. It
is also known as the negative output gap. The gap denotes the amount by which
aggregate demand must increase to increase the level of equilibrium at full
level of employment.
Thank You
Author- Kaushal Shah
Kautilya
IBS Mumbai
Comments
Post a Comment